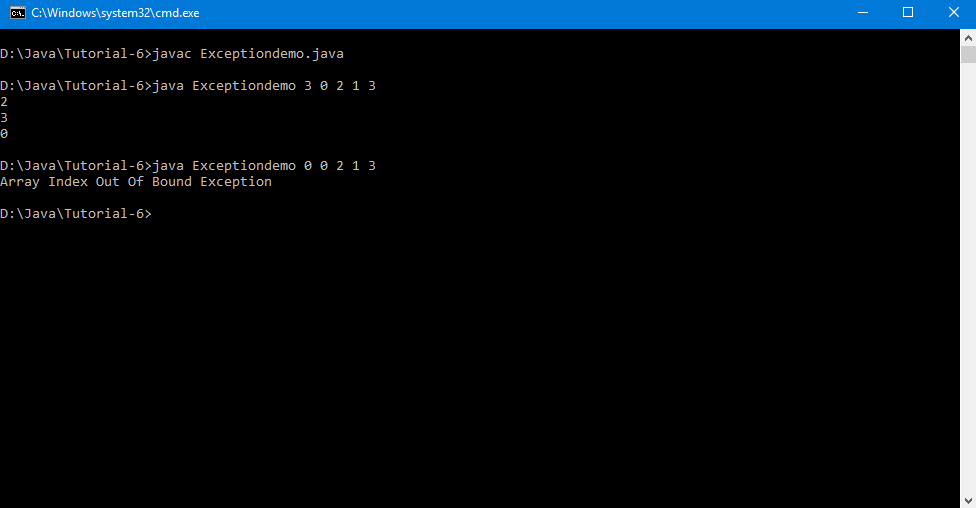
1. Write a program to insert values into an array.
The user will enter a sequence of index and value to be stored at that index on the command line.
Define your exception handlers for the following cases:
Index is out of range.
Value < 0 and value > 5000.
Given index has already value stored.
class Exceptiondemo
{
public static void main(String ar[])
{
int a[]=new int[Integer.parseInt(ar[0])];
int i,j=2,k;
try{
for(i=1,k=0;i<ar.length;i+=2,k++)
{
a[Integer.parseInt(ar[i])]=Integer.parseInt(ar[j]);
if(a[k]<0 || a[k]>5000)
{
throw new InvalidValueException();
}
j+=2;
}
for(i=0;i<a.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("Array Index Out Of Bound Exception");
}
catch(InvalidValueException ex)
{
System.out.println(ex.toString());
}
}
}
class InvalidValueException extends Exception
{
public String toString()
{
return ("Invalid Value Exception / 0 value is already there in array");
}
}
Output
2. Write a program to get the date in form of DD MM YYYY from command line argument.
Raise and handle following custom exceptions to check the validity of the entered date.
YearException: to check for valid four digit year.
MonthException: to check whether the month is between 01 to 12 or not.
DateException: to check wether date is between 01 to 31 or not.
It also checks the validity if date of month February when there is a leap year.
class YearException extends Exception
{
YearException()
{
System.out.println("Year Exception Generated");
}
public String toString()
{
return "Invalid Year";
}
}
class MonthException extends Exception
{
MonthException()
{
System.out.println("Month Exception Generated");
}
public String toString()
{
return "Invalid Month";
}
}
class DateException extends Exception
{
DateException()
{
System.out.println("Date Exception Generated");
}
public String toString()
{
return "Invalid Date";
}
}
class ddmmyyyy
{
public static void main(String a[])
{
int yyyy=Integer.parseInt(a[2]);
int mm=Integer.parseInt(a[1]);
int dd=Integer.parseInt(a[0]);
try
{
if(a.length==3)
{
//YEAR
if(a[2].length()!=4 || yyyy<1000 || yyyy>9999)
{
throw new YearException();
}
else
{
System.out.println("Year: "+yyyy);
}
//MONTH
if(a[1].length()!=2 || mm<01 || mm>12)
{
throw new MonthException();
}
else
{
System.out.println("Month: "+mm);
}
//DATE
if(a[0].length()!=2)
{
throw new DateException();
}
else if(mm==01 || mm==03 || mm==05 || mm==07 || mm==8 || mm==10 || mm==12)
{
if(dd<01 || dd>31)
{
throw new DateException();
}
else
{
System.out.println("Date: "+dd);
}
}
else if(mm==04 || mm==06 || mm==9 || mm==11)
{
if(dd<01 || dd>30)
{
throw new DateException();
}
else
{
System.out.println("Date: "+dd);
}
}
else if(mm==02)
{
if((yyyy%4==0) && (yyyy%100!=0) || (yyyy%400==0))
{
if(dd<01 || dd>29)
{
throw new DateException();
}
else
{
System.out.println("Date: "+dd);
}
}
else
{
if(dd<01 || dd>28)
{
throw new DateException();
}
else
{
System.out.println("Date: "+dd);
}
}
}
}
}
catch(YearException y)
{
System.out.println(y.toString());
}
catch(MonthException m)
{
System.out.println(m.toString());
}
catch(DateException d)
{
System.out.println(d.toString());
}
}
}
Output
3. Write a method for computing x & y by doing repetitive multiplication. x and y are of type integer and are to be given as command line arguments.
Raise and handle exception(s) for invalid values of x and y. Also define method main.
class InvalidNumberException extends Exception
{
InvalidNumberException()
{
System.out.println("Power Is Negative ");
}
}
class power
{
public static void main(String a[])
{
int x=Integer.parseInt(a[0]);
int y=Integer.parseInt(a[1]);
int temp;
try
{
if(y>=0)
{
if(y==0)
{
System.out.println(+x+" Power "+y+" is: "+1);
}
else
{
temp=x;
int i;
for(i=1;i<y;i++)
{
temp=temp*x;
}
System.out.println(+x+" Power "+y+" is: "+temp);
}
}
else if(y<0)
{
throw new InvalidNumberException();
}
}
catch(InvalidNumberException i)
{
double temp1;
int y1=(-y);
temp1=1/(double)x;
for(int j=1;j<y1;j++)
{
temp1=temp1*(1/(double)x);
}
System.out.println(+(double)x+" Power "+y+" is: "+temp1);
}
}
}
Output
4. Declare a class called coordinate to represent 3 dimensional Cartesian coordinates( x, y and z). Define following methods:
Constructors.
display method, to print values of members
add_coordinates method, to add three such coordinate objects to produce a resultant coordinate object.
Generate and handle exception if x, y and z coordinates of the result are zero.
main method, to show use of above methods.
class zerovalue extends Exception{}
class coordinate
{
float x,y,z;
coordinate()
{
x=0;
y=0;
z=0;
}
coordinate(float x,float y,float z)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
this.z=z;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println("X: "+x);
System.out.println("Y: "+y);
System.out.println("Z: "+z);
}
void add_coordinates(coordinate obj1,coordinate obj2)
{
this.x=this.x+obj1.x+obj2.x;
this.y=this.y+obj1.y+obj2.y;
this.z=this.z+obj1.z+obj2.z;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
coordinate c1=new coordinate(1,1,1);
coordinate c2=new coordinate(2,2,2);
coordinate c3=new coordinate(-3,3,3);
c1.add_coordinates(c2,c3);
coordinate c4=new coordinate();
c4=c1;
c4.display();
try
{
if(c4.x==0||c4.y==0||c4.z==0)
{
throw new zerovalue();
}
}
catch(zerovalue r)
{
System.out.println("Exception.No Co-Ordinate of Resultant Object Can Be Zero");
}
}
}
Output







0 comments:
Post a Comment